POP3 is useful when you only pick up your mail in one location. Messages in POP3 are usually deleted on the server once they are downloaded, so they cannot be read from multiple locations and will not be available in WebMail.
IMAP is used by a mail client to manage messages on the server. Mail clients on multiple computers can be configured to manage the same mailbox, perhaps your computer at work and your computer at home. Since the messages remain on the server, the Web Mail interface can also be used to manage them from any computer on the Internet. The disadvantage to using IMAP is that Microsoft Outlook and other clients will only "strikeout" messages as they are marked for deletion. An extra step of "purging deleted messages" (under the edit menu in Outlook) is necessary to actually delete the marked messages from the server.
If you only need to pick up your mail on one computer, POP3 is fine. But if you need to configure more than one computer to check your mail, or you want to use our Web Mail client when you are away from your own computer, then you will need to configure IMAP.
Microsoft Outlook Settings (most others are very similar)
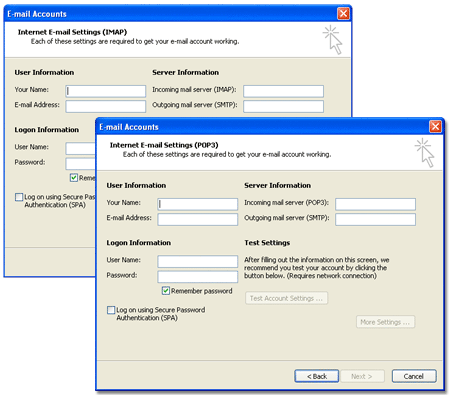
Since Microsoft outlook is the most popular mail client in the business world we discuss those settings. Most other mail clients have almost identical settings. You can see in the figures above that the settings for POP3 and IMAP in Microsoft Outlook are very similar, in fact the only real difference is that IMAP does not have the "Test Settings" feature. The field settings are:
| Setting | Value |
| User Name | This should be your real name. This shows up in the "from" field in the recipient's mail client, but it is not the email address that they will reply to. |
| E-mail Address | This is your e-mail address where others may send mail to you. This shows up as the "reply-to" address in messages you send. |
| Incoming mail server | This is the name or numeric address of the server to pick up mail from. In our hosting environment will be "mail.<your domain name>". |
| Outgoing mail server | In response to spam (unsolicited commercial e-mail) and the new Federal laws dealing with it in the United States, almost all Internet Service Providers have blocked their customers from directly sending outbound mail. Instead it must be relayed through a server that the ISP provides so that they can watch for bulk e-mail traffic. Check with your ISP to get the name of a server that you can relay through. If you send to an e-mail client list, such as a newsgroup, you may need to make arrangements with your ISP so they don't block the traffic. |
| User Name | This is the name used to login to the incoming mail server. In our environment use your email address "yourname@yourdomain". |
| Password | The secret password to enter your account. |
| Remember Password | Check this box unless you want to enter your password every time the program checks mail. |
| Log on using SPA | Leave this box unchecked; our mail servers do not support Secure Password Authentication. |
Account Administrator's Notes:
![]() Two mailboxes
are automatically created for each domain, postmaster
and webmaster.
You need to pick up the messages from these mailboxes or forward them to a mailbox
that is picked up. To change the settings
log on to the control panel for
your account, and click on the email icon (pictured at the right).
Two mailboxes
are automatically created for each domain, postmaster
and webmaster.
You need to pick up the messages from these mailboxes or forward them to a mailbox
that is picked up. To change the settings
log on to the control panel for
your account, and click on the email icon (pictured at the right).
Help for managing e-mail mailboxes and users is available here as part of the H-Sphere control panel documentation.




